In Java, there exist multiple approaches to swap the values of two numbers. Typically, we can utilize the swap() method provided by the Math class or employ a temporary variable as an intermediary step to exchange the values. In addition to these conventional methods, another way to swap two numbers is by utilizing the bitwise XOR operator (^) or by using division and multiplication operations.
In this section, our focus will be on developing a Java program that swaps two numbers using the bitwise XOR operator (^).
Using Bitwise Operator
The bitwise XOR operator, denoted by the symbol (^), is a commonly used technique for swapping two numbers. It operates by comparing the bits of two operands and returns 0 (false) if the bits are equal, and 1 (true) if they are not equal. The truth table for the XOR operator is as follows:
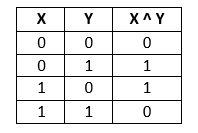
To swap two numbers without using the swap() method or a third variable in Java, we can utilize the bitwise XOR operator. The following steps outline the process:
- Convert the given variables, X and Y, into their binary equivalents.
- Compute the XOR of X and Y and store the result in X, i.e., X = X ^ Y.
- Once again, calculate the XOR of X and Y and assign the result to Y, i.e., Y = X ^ Y.
- Finally, calculate the XOR of X and Y and store the result in X, i.e., X = X ^ Y.
- By completing these steps, the values of X and Y will be swapped.
Example: Swap the variables X = 5 and Y = 9 using the bitwise operator.
Solution:
Step 1: Binary equivalent of the variables X and Y are:
X = 5 = 0101 and Y = 9 = 1001
Step 2: Find X = X ^ Y.
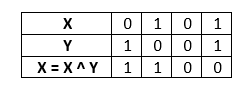
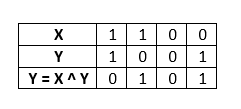
Step 3: Find Y = X ^ Y.
Step 4: Find X = X ^ Y.
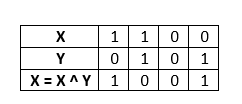
After completing these steps, the values of X and Y have been successfully swapped. So, X now holds the value 9, and Y holds the value 5.
X = 9 and Y = 5
SwapTwoNumbersExample1.java
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SwapTwoNumbersExample
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a, b;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the first number: ");
a = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter the second number: ");
b = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("Before swapping:");
System.out.println("a = " +a +", b = " +b);
a = a ^ b;
b = a ^ b;
a = a ^ b;
System.out.println("After swapping:");
System.out.print("a = " +a +", b = " +b);
}
}
Output:
Enter the first number: 5 Enter the second number: 9 Before swapping: a = 5, b = 9 After swapping: a = 9, b = 5
SwapTwoNumbersExample2.java
public class SwapTwoNumbersExample1
{
static void swapNumbers(int x, int y)
{
System.out.println("Before swapping");
System.out.println("x= " + x + ", y= " + y);
x = x ^ y;
y = x ^ y;
x = x ^ y;
System.out.println("After swapping");
System.out.println("x= " + x + ", y= " + y);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x = 12;
int y= 34;
swapNumbers(x,y);
}
}
Output:
Before swapping x= 12, y= 34 After swapping x= 34, y= 12
Using Multiplication and Division
SwapTwoNumbersExample3.java
public class SwapTwoNumbersExample2
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int x = 10;
int y = 20;
System.out.println("values before swapping:");
System.out.println("x = " + x +" y = " + y);
//swapping two numbers using multiplication and division
x = x*y; //now x is 200
y = x/y; //now x is 200 and y is 20, on dividing x/y is y=10 (original value of x)
x = x/y; //now x is 200 and y is 10, on dividing x/y is x=20 (original value of y)
System.out.println("values after swapping:");
System.out.println("x = " + x +" y = " + y);
}
}
Output:
values before swapping: x = 10 y = 20 values after swapping: x = 20 y = 10
To discover more valuable information, such as the Swap Two Numbers Using Bitwise Operator Program, be sure to follow tutorials.freshersnow.com.
