In this tutorial, we are going to study the RecordReader in Hadoop MapReduce. We will discuss the introduction to Hadoop RecordReader, working on RecordReader. We will also study the types of RecordReader in MapReduce, the size of the single Record in Hadoop MapReduce in this MapReduce Tutorial.
What is RecordReader in MapReduce?
A RecordReader transforms the byte-oriented view of the input to a record-oriented view for the Mapper and Reducer tasks for processing.
To understand Hadoop RecordReader, we want to understand MapReduce Dataflow. Let us discuss how the data flow:
MapReduce is an effortless model of data processing. Inputs and outputs for the map and decrease functions are key-value pairs. Below is the general form of the map and reduce functions:
• Map: (K1, V1) → list (K2, V2)
• Reduce: (K2, list (V2)) → list (K3, V3)
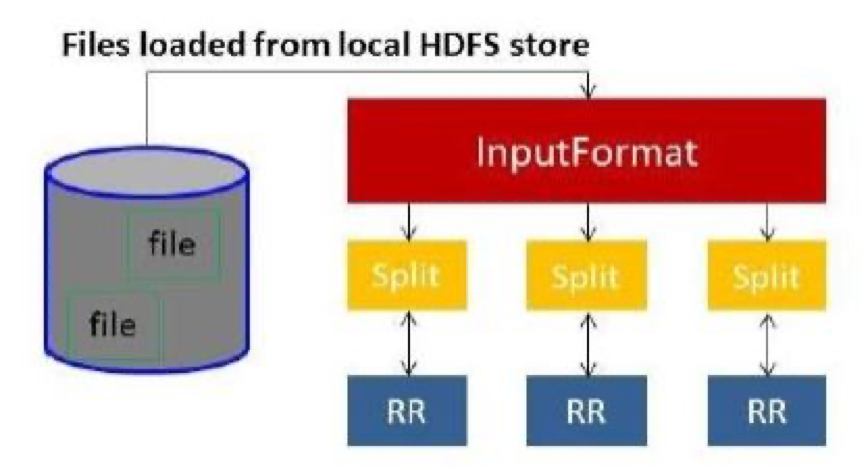
Now before processing starts, it requires knowing which data to process. Therefore, the InputFormat class assists to achieve this. This class selects the file from HDFS that is the input to the map function. It is also accountable for creating the input splits. Additionally, divide them into records. It splits the data into the number of splits (typically 64/128mb) in HDFS. This is known as InputSplit. InputSplit is the logical representation of data. In a MapReduce job, the execution number of map tasks is similar to the number of InputSplits.
By calling ‘getSplit ()’ the client calculates the splits for the job. Then it sent to the application master. It utilizes their storage locations to schedule map tasks that will handle them on the cluster.
After that map task permits the split to the createRecordReader() method. From that, it gets RecordReader for the split. RecordReader creates a record (key-value pair). Then it passes to the map function.
Hadoop RecordReader in MapReduce job execution utilizes the data within the boundaries that are being generated by the inputsplit. And it then generates Key-value pairs for the mapper. The “start” is the byte location in the file. In the beginning, Hadoop RecordReader starts creating key/value pairs. The “end” is where RecorReader stops reading records. In RecordReader, the data is uploaded from its source. Then the data are transformed into key-value pairs suitable for reading by the Mapper. It interacts with the inputsplit until the file reading is not completed.
How RecorReader works in Hadoop MapReduce?
It is more than iterator over the records. The map task uses one record to generate key-value pairs which it passes to the map function. We can also see this by using the mapper’s run function given below:
public void run(Context context ) throws IOException, InterruptedException{
setup(context);
while(context.nextKeyValue())
{
map(context.setCurrentKey(),context.getCurrentValue(),context)
}
cleanup(context);
}
Although RecordReader doesn’t need to stay in between the boundaries created by the inputsplit to generate key-value pairs it usually stays. Moreover, custom implementation can even read more data outside of the inputsplit.
Then, after running setup(), the nextKeyValue() will reiterate on the context. This generates the key and value objects for the mapper. By way of context, the framework retrieves key-value from record reader. Then pass to the map() method to do its job. Therefore, input (key-value) to the map function handles as per the logic mentioned in the map code. When the record moves to the end of the record, the nextKeyValue() method returns false.
Types of RecordReader
InputFormat defines the RecordReader instance, in Hadoop. By default, using TextInputFormat ReordReader transforms data into key-value pairs. TextInputFormat also offers 2 types of RecordReaders which as below:
1. LineRecordReader
It is the default RecordReader. TextInputFormat offers this RecordReader. It also considers each line of the input file as the new value. Then the associated key is byte offset. It always hops the first line in the split (or part of it), if it is not the first split. It always reads one line after the boundary of the split in the end (if data is available, so it is not the last split).
2. SequenceFileRecordReader
This Hadoop RecordReader reads data stated by the header of a sequence file.
The maximum size of the single Record
By using the below parameter we set the maximum value.
1.conf.setInt(“mapred.linerecordreader.maxlength”, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
Conclusion
In conclusion, Hadoop RecordReader generates the input (key-value) to Mapper. It also utilizes TextInputFormat for transforming data into key-value pairs.
