In Java, the Krishnamurthy number, also known as a Strong number, is a special type of number. It is defined as a number whose sum of the factorials of its digits is equal to the number itself. Similar to Prime and Armstrong numbers, Krishnamurthy numbers are often featured in interviews as Strong numbers.
To determine whether a number is a Krishnamurthy number, the following steps can be followed:
- Take a number as input.
- Calculate the factorial of each digit in the number.
- Sum up the factorials of all the digits and store the result in a separate variable.
- Compare the sum of the factorials with the original number.
- If the sum of the factorials is equal to the original number, then the number is considered a Krishnamurthy number.
Example:
Number = 145 = 1! + 4! + 5! = 1 + ( 4 * 3 * 2 * 1 ) + ( 5 * 4 * 3 * 2 * 1 ) = 1 + 24 + 120 = 145
KrishnamurthyNumber.java
//import required classes and packages
import Java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
//create KrishnamurthyNumber class to check whether the given number is a Krishnamurthy number or not
class KrishnamurthyNumber {
// create fact() method to calculate the factorial of the number
static int fact(int number)
{
int f = 1;
while (number != 0) {
f = f * number;
number--;
}
return f;
}
// create checkNumber() method that returns true when it founds number krishnamurthy
static boolean checkNumber(int number)
{
int sum = 0; //initialize sum to 0
int tempNumber = number; //create a copy of the original number
//perform operation until tempNumber will not equal to 0
while (tempNumber != 0) {
// calculate the factorial of the last digit of the tempNumber and then add it to the sum
sum = sum + fact(tempNumber % 10);
// replace the value of tempNumber by tempNumber/10
tempNumber = tempNumber / 10;
}
// Check whether the number is equal to the sum or not. If both are equal, number is krishnamurthy number
if(sum == number)
return true;
else
return false;
}
// main() method start
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n; //initialize variable n
//create scanner class object to read data from user
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
//custom message
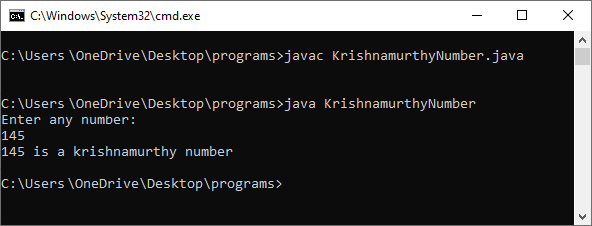
System.out.println("Enter any number:");
//store user entered value into variable n
n = sc.nextInt();
if (checkNumber(n))
System.out.println(n + " is a krishnamurthy number");
else
System.out.println(n + "is not a krishnamurthy number");
}
}
Output
FindAllKrishnamurthyNumber.java
//import required classes and packages
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
//create FindAllKrishnamurthyNumber class to get all the Krishnamurthy number in a given range
class FindAllKrishnamurthyNumber
{
//main() method start
public static void main(String args[])
{
int range;
//create scanner class object
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
//show custom message
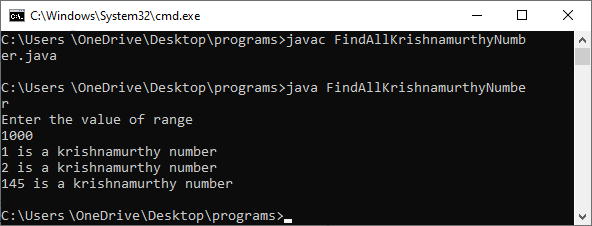
System.out.println("Enter the value of range");
//store user entered value into variable range
range = sc.nextInt();
for(int i = 1; i <= range; i++)
checkNumber(i);
}
// create fact() method to calculate the factorial of the number
static int fact(int number)
{
int f = 1;
while (number != 0) {
f = f * number;
number--;
}
return f;
}
// create checkNumber() method to check krishnamurthy number
static void checkNumber(int number)
{
int sum = 0; //initialize sum to 0
int tempNumber = number; //create a copy of the original number
//perform operation until tempNumber will not equal to 0
while (tempNumber != 0) {
// calculate the factorial of the last digit of the tempNumber and then add it to the sum
sum = sum + fact(tempNumber % 10);
// replace the value of tempNumber by tempNumber/10
tempNumber = tempNumber / 10;
}
// Check whether the number is equal to the sum or not. If both are equal, the number is Krishnamurthy number
if(sum == number)
System.out.println(number + " is a krishnamurthy number");
}
}
Output
For further knowledge on topics such as Krishnamurthy Number in Java, visit tutorials.freshersnow.com.
