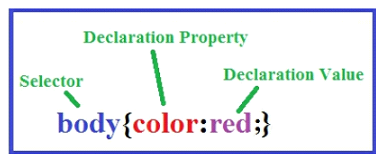
CSS Rule: When you style your webpage, you are basically adding a set of “style rules” to your webpage. These style rules are called “CSS rules”. Each CSS rule is made up of two main parts: a “selector”, and one or more “declarations”.
CSS Syntax
NOTE: Each declaration ends with a semicolon.
The Selector
The selector names the HTML element that you want to style. For example, a selector of “h1” means we want to apply the style rules to the main header, i.e., the content between the <h1></h1> tags. CSS selectors can be an HTML element name, a class name, or an id name. (We will talk about “classes and “ids” later.)
CSS Declaration
The declaration is essentially a “style rule” because it defines the style that you want to apply to the selected HTML element. Each declaration is a “property-value” pair. The “property” defines the style attribute that you want to change, such as “color” or “font-size”. Each property is given a value, such as “red” or “15px”.
NOTE: The abbreviation “px” is short for “pixels”, a type of measurement. A pixel is a dot on the computer screen.
CSS Syntax Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
p {
color: blue;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>Tutorials.freshersnow</p>
<p>A basic example of CSS</p></body>
</html>