What is an Automorphic Number?
An automorphic number is defined as a number that satisfies the condition that its square ends with the same digits as the original number. In simpler terms, an automorphic number’s square has a suffix that matches the original number.
For instance, consider the number 25. When we square 25, we get 625. Notice that the last two digits of the square (25) match the original number. Therefore, 25 is an automorphic number. Similarly, the number 76 is automorphic because its square is 5776, and the last two digits (76) represent the number itself.
Automorphic numbers can be found in various forms, such as single-digit numbers like 5 and 6, as well as larger numbers like 36 and 890625. These numbers have the property that their squares end with the same digits as the original number.
To determine whether a given number is automorphic or not, we can analyze its square and check if the suffix matches the original number.
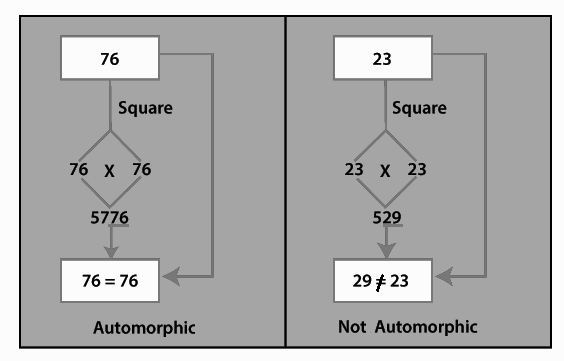
How to find automorphic number?
Here are the steps to determine if a given number is an automorphic number:
- Read a number (num) from the user.
- Calculate the square of the given number and store it in a variable (square).
- Extract the last digit(s) of the square.
- Compare the last digit(s) of the square with the original number (num).
- If the last digit(s) of the square and num are not equal, the given number is not an automorphic number.
- If the last digit(s) of the square and num are the same, proceed to the next step.
- Remove the last digit of the original number (num).
- Repeat steps 3 to 7 until the original number (num) becomes 0.
Java Automorphic Number Program
AutomorphicNumberExample.java
public class AutomorphicNumberExample
{
//user-defined static method that checks whether the number is automorphic or not
static boolean isAutomorphic(int num)
{
//determines the square of the specified number
int square = num * num;
//comparing the digits until the number becomes 0
while (num > 0)
{
//find the remainder (last digit) of the variable num and square and comparing them
if (num % 10 != square % 10)
//returns false if digits are not equal
return false;
//reduce num and square by dividing them by 10
num = num/10;
square = square/10;
}
return true;
}
//Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
//number to be check
//calling the method and prints the result accordingly
System.out.println(isAutomorphic(76) ? "Automorphic" : "Not Automorphic");
System.out.println(isAutomorphic(13) ? "Automorphic" : "Not Automorphic");
}
}
Output:
Automorphic Not Automorphic
AutomorphicNumberExample1.java
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AutomorphicNumberExample1
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a number to check: ");
//reading a number from the user
int num = in.nextInt();
int count=0;
//determines the square of the given number
int square = num*num;
//copying the variable num into temp
int temp = num;
//iterate over the variable num until the condition become false
while(temp>0)
{
count++;
//removes last digit of the variable num
temp=temp/10;
}
//determines the last digit of the variable square
int lastDigit = (int) (square%(Math.pow(10, count)));
//compare num with last digit of the variable square
if(num == lastDigit)
System.out.println(num+ " is an automorphic number.");
else
System.out.println(num+ " is not an automorphic number.");
}
}
Output 1:
Enter a number to check: 625 625 is an automorphic number.
Output 2:
Enter a number to check: 312 312 is not an automorphic number.
AutomorphicNumberExample2.java
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AutomorphicNumberExample2
{
//user-defined static method that checks whether the number is automorphic or not
private static boolean isAutomorphic(int num)
{
int count=0;
//determines the square of the given number
int square = num*num;
//copying the variable num into temp
int temp = num;
//iterate over the variable num until the condition become false
while(temp>0)
{
count++;
//removes last digit of the variable num
temp=temp/10;
}
//determines the last digit of the variable square
int lastDigit = (int) (square%(Math.pow(10, count)));
//compare the last digit with num
return num == lastDigit;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int start, end;
System.out.print("Enter the starting value: ");
start = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter the ending value: ");
end = in.nextInt();
System.out.println("Automorphic numbers between "+start+" and "+end+" are: ");
//the for loop starts from the starting value and execute until the condition becomes false
for(int i=start; i<=end; i++)
{
//calling the user-defined method
if(isAutomorphic(i))
//prints the number if it is automorphic
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
}
}
Output:
Enter the starting value: 1 Enter the ending value: 10000 Automorphic numbers between 1 and 10000 are: 1 5 6 25 76 376 625 9376
Follow tutorials.freshersnow.com to learn more, such as the Automorphic Number Program.
