In order to carry out an ARP poisoning attack and redirect packet flow through our device, we will use a program called arpspoof, which is part of the dsniff suite. This suite includes various tools that can be utilized for conducting MITM attacks. In this tutorial, we will demonstrate how to use the arpspoof tool specifically to perform ARP poisoning.
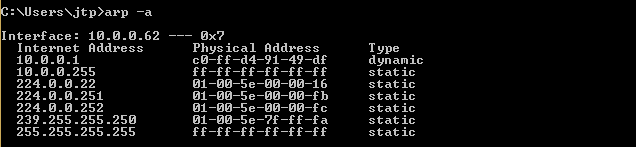
To view the ARP table on the target Windows device, we can execute the command “arp -a” in the command prompt. As shown in the screenshot, the table displays the MAC address of the access point, which is associated with the IP address 10.0.0.1 and is identified as “c0-ff-d4-91-49-df”.
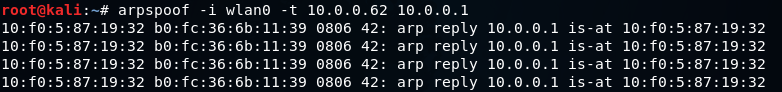
Now that we are connected to the target network, we will utilize the arpspoof tool to launch our ARP poisoning attack. By specifying the “-i” flag, we can select the appropriate network interface for the attack – in this case, “wlan0”. We will then provide the IP address of our target Windows device, which is “10.0.0.62”, and the IP address of the access point, which is “10.0.0.1”. This will allow us to inform the access point that our MAC address is associated with the client IP address, essentially tricking it into thinking that we are the target client.
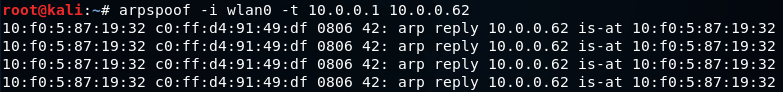
Following the initial execution of arpspoof, we will run the tool once more, but with a reversal of the IP addresses. Instead of convincing the access point that our MAC address is associated with the client IP address, we will inform the client that our MAC address is associated with the access point’s IP address. This allows us to impersonate the access point and intercept all traffic between the client and the access point.
By executing both of the previous commands, we will successfully deceive both the client and the access point, allowing all packets to flow through our device. This will enable us to intercept and analyze all traffic exchanged between the two devices, which is the objective of the ARP poisoning attack.
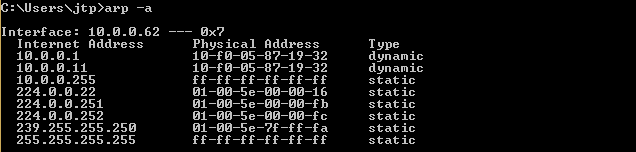
Upon executing the ARP poisoning attack, we will observe that the MAC address associated with the target access point has been modified. As displayed in the screenshot, the original MAC address “c0-ff-d4-91-49-df” has been replaced with “10-f0-05-87-19-32”, which corresponds to the MAC address of our Kali machine.
To ensure that packets are not dropped when they flow through our device, we will activate IP forwarding. This allows each packet to be properly forwarded to its intended destination. Specifically, any packets received from the client will be sent to the router, and any packets received from the router will be transmitted to the client without being discarded by our device. The IP forwarding feature can be enabled using the following command:
![]()
As a result of the ARP poisoning attack, the Windows device will be under the impression that our attacker device is the access point. Consequently, all requests made by the Windows device to communicate with the access point will be redirected to our attacker device, placing it in the middle of the connection. This will allow us to view, modify, or discard all packets transmitted between the two devices.
To know more details like ARP Spoofing using arpspoof, do follow us daily @ tutorials.freshersnow.com.
